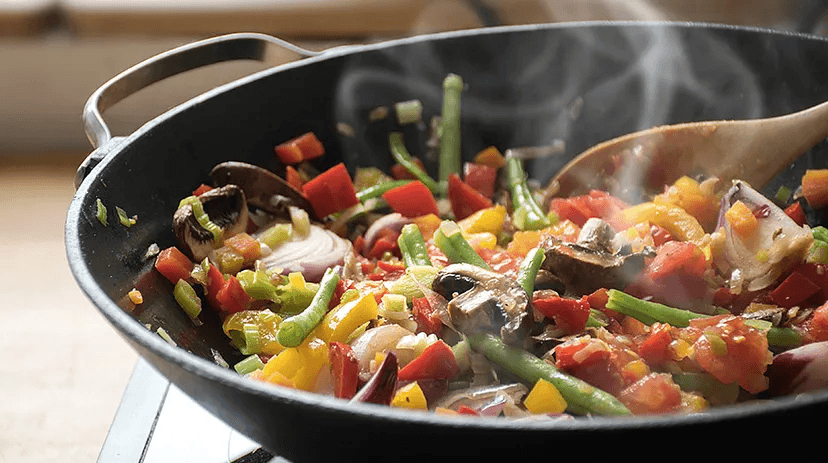
Cooking is central to transforming raw ingredients into delicious meals, but the process can significantly alter their nutritional value. Vitamins and minerals are crucial for maintaining health, supporting immunity, and preventing chronic diseases.
However, the cooking method you choose can influence how much of these nutrients remain in your food.
A study published revealed that some cooking methods could reduce the nutrient content of vegetables. Understanding these effects can help you make informed decisions to maximize the nutritional benefits of your meals.
How Cooking Affects Nutrient Content
1. The Role of Heat, Water, and Time
- Heat: High temperatures can break down heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C and certain B vitamins.
- Water: Water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex vitamins can leach into cooking water.
- Duration: Longer cooking times generally result in more nutrient loss.
2. Water-Soluble vs. Fat-Soluble Vitamins
- Water-Soluble Vitamins: Easily lost in water-based cooking methods.
- Fat-Soluble Vitamins (A, D, E, K): Generally more stable during cooking but may degrade with prolonged heat exposure.
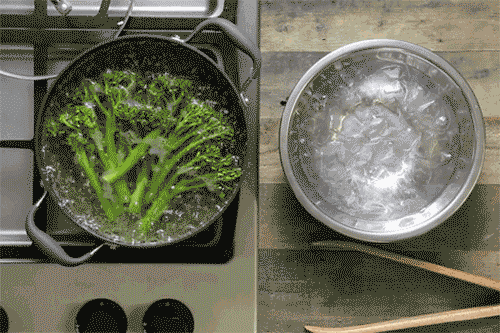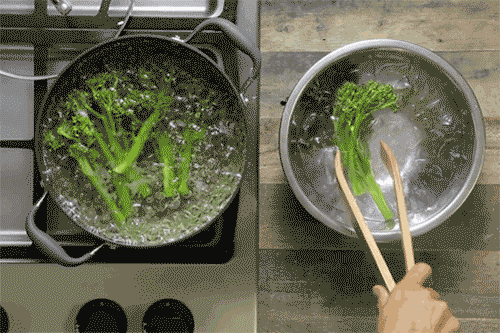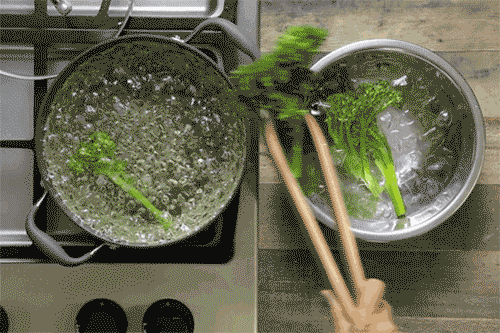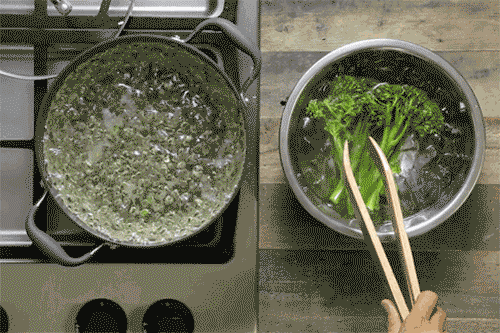
Common Cooking Methods and Their Impact

Nutrient-Specific Changes
1. Vitamin C
- Highly sensitive to heat, light, and oxygen.
- Example: Boiling broccoli can reduce its vitamin C content by up to 50%, while steaming preserves most of it.
2. B Vitamins
- Found in whole grains, eggs, and meats, these are vulnerable to both heat and water.
- Cooking meats at high temperatures can degrade thiamine (B1) and pyridoxine (B6).
3. Minerals
- Relatively stable during cooking but can leach into cooking liquids.
- Example: Boiling spinach can result in a 40% reduction in calcium content due to mineral leaching.

Tips to Preserve Nutrients While Cooking
- Cook with Minimal Water: Use steaming or microwaving instead of boiling to reduce nutrient loss.
- Shorter Cooking Times: Overcooking leads to significant nutrient degradation. Aim for al dente vegetables.
- Reuse Cooking Water: Use leftover water from boiling vegetables in soups or sauces to retain water-soluble nutrients.
- Cut Vegetables Right Before Cooking: Minimize nutrient loss from exposure to air and light by cutting only as needed.
- Cook with the Skin On: Many nutrients are concentrated in or just below the skin of vegetables and fruits.
Tip: Pair vegetables with healthy fats like olive oil to enhance the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Cooking methods significantly affect the vitamin and mineral content of our food. While no single method is perfect, choosing techniques like steaming or microwaving can help maximize nutrient retention.

Cooking isn’t just about taste — it’s about maximizing the benefits of the food we eat.









